Stroke Care
Home Instead’s highly trained caregivers can help your family find your new normal.


Stroke Care Services In Singapore
No one expects a stroke to occur, but when it does, our caregivers are passionate about delivering important in-home stroke care.
More Information on Stroke Care
According to the Singapore National Stroke Association, a stroke occurs when blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted. This event results in brain damage. Functions which are normally controlled by the damaged brain become affected suddenly and will not function properly. As stroke is a potentially life-threatening disease, it is important to seek early treatment.
The Singapore National Stroke Association encourages the use of the FAST test to check for the most common symptoms of a stroke.
Face: Smile and see if one side of the face droops.
Arms: Raise both arms. Does one arm drop down?
Speech: Say a short phrase and check for slurred or strange speech.
Time: If the answer to any of these is yes, call 996 right away and write down the time when symptoms started.
Acting F.A.S.T. can help stroke patients get the treatment they desperately need. The stroke treatments that work best are available only if the stroke is recognized and diagnosed within 3 hours of the first symptoms. Stroke patients may not be eligible for these if they don’t arrive at the hospital in time. Stay vigilant and save a life.

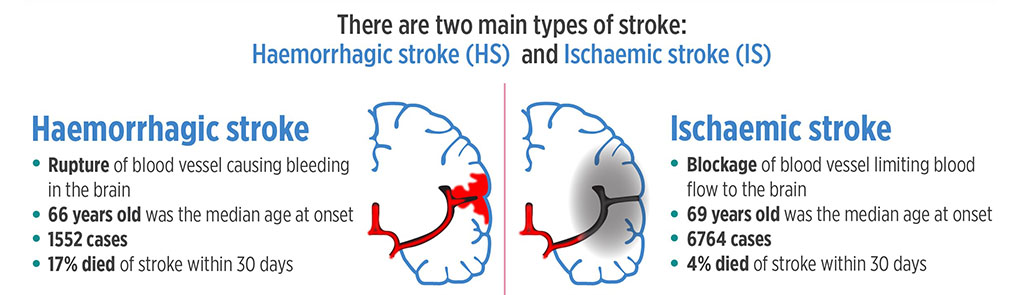
In Singapore, according to the Singapore Stroke Registry, the number of stroke episodes increased from 5,890 episodes in 2010 to 8,849 episodes in 2019 and we can expect this to increase as our population ages. The majority of cases was Ischaemic Stroke (6764) followed by Haemorrhagic Stroke (1552).
Warning Signs
Sometimes a stroke happens gradually, but there is likely to be one or more sudden symptoms like these:
Numbness or weakness in face, arm, or leg, especially on one side
Confusion or trouble understanding other people
Difficulty speaking
Trouble seeing with one or both eyes
Problems walking or staying balanced or coordinated
Dizziness
Severe headache that comes on for no reason
Home Instead In-Home Stroke Care
When someone experiences a stroke, their physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being can each be impacted and require nurturing if the individual is going to thrive in their new reality. Stroke survivors may experience physical changes from minor weakness to partial paralysis which may lead to mobility and ambulation challenges. Inability to coordinate and balance well can make previously simple tasks difficult, if not impossible to accomplish. In addition to the physical changes, stroke survivors may also see a cognitive and emotional decline after the stroke. In this difficult period, most family members if not prepared for the sudden responsibility of being a caregiver, are uncertain how to overcome the fear and anxiety they may experience.
Post Stroke Activities and Benefits
A Home Instead Professional Care Pro can provide the support one needs during this transition, including:
Encouragement to do as much as they can on their own
Personal care assistance, such as toileting, bathing and grooming
Maintain a routine to discourage agitation and outbursts
Mental stimulation through conversation and other activities
Maintaining a safe environment
Honor who the senior was earlier in life
Provide nutritious meals and feeding assistance
Assist with ambulation and socialization
Transport to medical appointments and other events
Support the family
Light housework and other household tasks
Pet care
Stroke Prevention
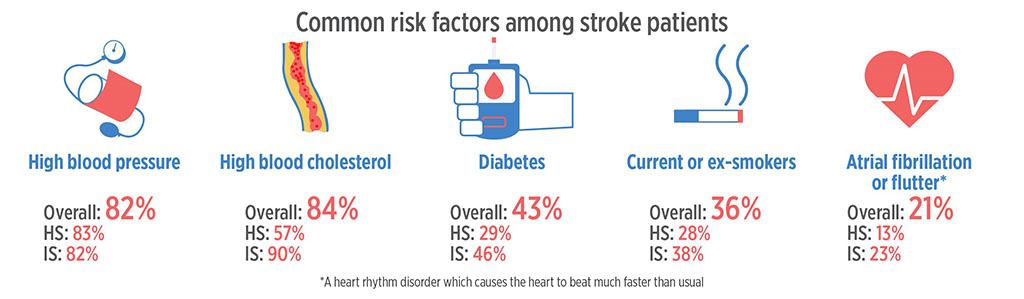
Many strokes are lifestyle related, so first understand the risks:

What is a Stroke and What Causes It?
Strokes are caused by a lack of blood flow to part of the brain which in turn causes a lack of oxygen and resulting temporary or permanent brain damage. The longer the interruption to blood flow, the more serious the damage, hence urgency to get treatment.
There are several types of Stroke. The following is summarised from The American Stroke Association:
Ischemic Stroke (Clot)
Occurs when a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain is obstructed. It accounts for 87 % of all strokes. Fatty deposits lining the vessel walls, called atherosclerosis, are the main cause for ischemic stroke. Fatty deposits can cause two types of obstruction:
Cerebral thrombosis is a thrombus (blood clot) that develops at the fatty plaque within the blood vessel.
Cerebral embolism is a blood clot that forms at another location in the circulatory system, usually the heart and large arteries of the upper chest and neck. Part of the blood clot breaks loose, enters the bloodstream and travels through the brain’s blood vessels until it reaches vessels too small to let it pass. A main cause of embolism is an irregular heartbeat called atrial fibrillation. It can cause clots to form in the heart, dislodge and travel to the brain.
Haemorrhagic Stroke (Bleeds)
Haemorrhagic strokes make up about 13 % of stroke cases. They’re caused by a weakened vessel that ruptures and bleeds into the surrounding brain. The blood accumulates and compresses the surrounding brain tissue.
The two types of haemorrhagic strokes are intracerebral (within the brain) hemorrhage or subarachnoid haemorrhage.
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures. Two types of weakened blood vessels usually cause hemorrhagic stroke: aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a cluster of abnormally formed blood vessels. Any one of these vessels can rupture, also causing bleeding into the brain.
An aneurysm is a ballooning of a weakened region of a blood vessel. If left untreated, the aneurysm continues to weaken until it ruptures and bleeds into the brain.
TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack)
Called a mini-stroke, it is caused by a serious temporary clot. This is a warning sign stroke and should be taken seriously.
TIA is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain. Since it does not cause permanent damage, it is often ignored. But this is a big mistake. TIAs may signal a full-blown stroke ahead.
The risk of having a full-blown stroke is highest in the 90 days following a TIA. About 9% to 17% of patients who have a TIA have a stroke within 90 days.
Anyone can have a TIA, but the risk increases with age. The risk factors are smoking, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and blood clots called embolisms. When a TIA occurs in a young person with no clear risk factors, the patient might be sent to a neurologist for testing to rule out vasculitis, carotid artery dissection and other types of injury or infection.
Cryptogenic Stroke
In most cases, a stroke is caused by a blood clot that blocks the flow of blood to the brain. In some instances, despite testing, the cause of a stroke cannot be determined. This is called a cryptogenic stroke.
Because approximately 1 in 4 stroke survivors will likely have another stroke event, finding the cause of the stroke will help the physician treat the cause of stroke and lower the likelihood of another.. Having a cryptogenic stroke may be frustrating and overwhelming, but with a proper diagnostic work-up and collaboration with the healthcare team, the stroke survivor can take part in finding the cause of stroke and help prevent stroke recurrence.
Brain Stem Stroke
When stroke occurs in the brain stem, it can affect both sides of the body and may leave someone in a ‘locked-in’ state. When a locked-in state occurs, the patient is generally unable to speak or move below the neck.
Brain stem strokes can have complex symptoms, and they can be difficult to diagnose. A person may have vertigo, dizziness and severe imbalance without the hallmark of most strokes — weakness on one side of the body. The symptoms of vertigo dizziness or imbalance usually occur together; dizziness alone is not a sign of stroke. A brain stem stroke can also cause double vision, slurred speech and decreased consciousness.
Only a half-inch in diameter, the brain stem controls all basic activities of the central nervous system: consciousness, blood pressure and breathing. All motor control for the body flows through it. Brain stem strokes can impair any or all of these functions. More severe brain stem strokes can cause locked-in syndrome, a condition in which survivors can move only their eyes.
If a stroke in the brain stem results from a clot, the faster blood flow can be restored, the better the chances for recovery. Patients should receive treatment as soon as possible for the best recovery.
Like all strokes, brain stem strokes produce a wide spectrum of deficits and recovery. Whether a survivor has minor or severe deficits depends on the location of the stroke within the brain stem, the extent of injury and how quickly treatment is provided.
Risk factors for brain stem stroke are the same as for strokes in other areas of the brain: high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, atrial fibrillation and smoking. Similarly, brain stem strokes can be caused by a clot or a haemorrhage. There are also rare causes, like injury to an artery due to sudden head or neck movements.
Recovery is possible. Because brain stem strokes do not usually affect language ability, the patient is often able to participate more fully in rehabilitation. Double vision and vertigo usually resolve after several weeks of recovery in mild to moderate brain stem strokes.

Michelle
"Judy from Home Instead helped me a lot. She kept me company and helped with everyday living tasks. Her companionship helped reduce any mental stress. Thank you Judy and Home Instead for the personalised service!"
Your Care Journey Starts Here
1
Get a free care consultation
Contact us for a free consultation.
2
Book appointment
Book an appointment.
3
Preparation
Receive the healthcare service you want.

Start Your Healthcare Journey Today.
Contact us for a free, no-obligation care consultation!
